

- CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE HOW TO
- CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE UPGRADE
- CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE SOFTWARE
- CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE PROFESSIONAL
- CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE FREE
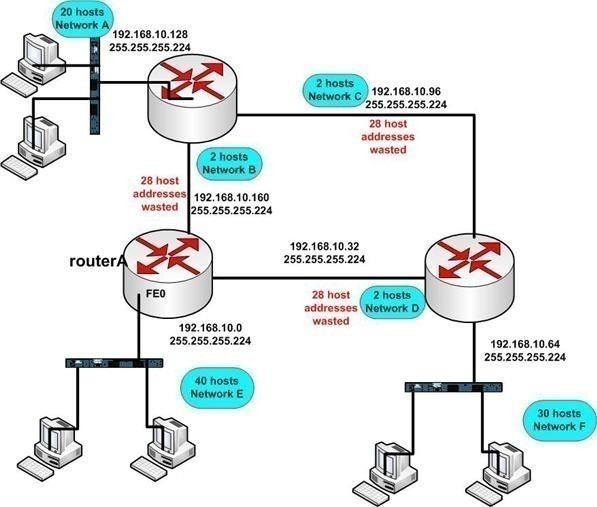
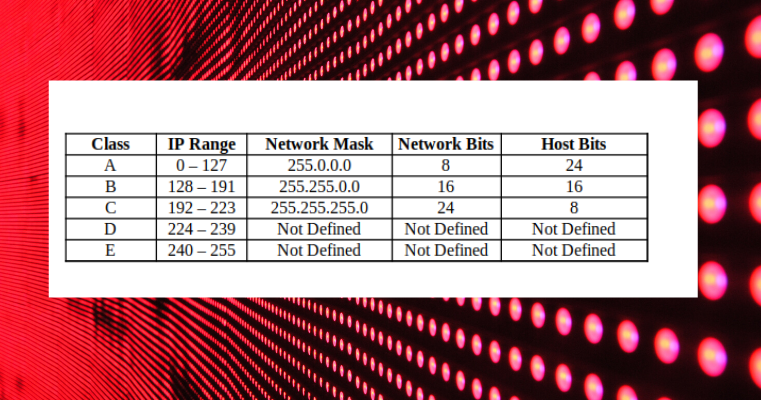
Since the internet must accommodate networks of all sizes, an addressing scheme for a range of networks exists based on how the octets in an IP address are broken down. The range of values in decimal is 0 to 255 because that represents 00000000 to 11111111 in binary. This results in the characteristic dotted decimal format for IP addresses-for example, 172.16.254.1. The 32 binary bits are divided into the host and network sections by the subnet mask but they are also broken into four 8-bit octets.īecause binary is challenging, we convert each octet so they are expressed in dot decimal. IP Address and Subnet MaskĪ 32-bit IP address uniquely identifies a single device on an IP network. The phrase “mask” is applied because the subnet mask essentially uses its own 32-bit number to mask the IP address. The goal of subnet masks are simply to enable the subnetting process. When organizations need additional subnetworking, subnetting divides the host element of the IP address further into a subnet. The IP address, subnet mask and gateway or router comprise an underlying structure-the Internet Protocol-that most networks use to facilitate inter-device communication. Neither can be assigned to hosts, as they are reserved for these special purposes. The “255” address is always assigned to a broadcast address, and the “0” address is always assigned to a network address. In this way, the subnet mask separates the IP address into the network and host addresses. This means that when a local device wants to send information to a device at an IP address on another network, it first sends its packets to the gateway, which then forwards the data on to its destination outside of the local network.Ī subnet mask is a 32-bit number created by setting host bits to all 0s and setting network bits to all 1s. The device called a gateway or default gateway connects local devices to other networks. The subnet mask splits the IP address into the host and network addresses, thereby defining which part of the IP address belongs to the device and which part belongs to the network. IP addresses are either configured by a DHCP server or manually configured (static IP addresses). << Back to Technical Glossary Subnet Mask DefinitionĮvery device has an IP address with two pieces: the client or host address and the server or network address. Glossary Get familar with related technical terms.Support Contact support to resolve issues.
CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE PROFESSIONAL
Professional Services Engage with professional services for migration and customization.Knowledge Base Get the best documentation on our product.LBTV Hits all major topics of modern load balancing.Virtual Summit Attend a quarterly summit to learn more.
Webinars Join our subject matter experts to explore a use case.Content Library Find everything related to multi-cloud load balancing.
CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE HOW TO
CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE FREE
CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE SOFTWARE
CLASS A SUBNET MASK TABLE UPGRADE


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
